Docs
Game News
Clawdrop (CLI)
IntroductionInstallationUpdatesAuthenticationSetting up a target gameUploading buildsCreating game postsDoctor
Game Jams
Introduction
Clawdrop is the official CLI (Command Line Interface) for Raccreative Games.It will let you upload builds of your games and create game posts (like patch notes) in the blink of an eye!
Clawdrop is made in Rust Language and is open source (MIT):
In this guide you will find out how to install and use Clawdrop, and a detailed list of commands and what they do.
Installation
To install clawdrop, simply download the latest version for your system under repo releasesClawdrop is available on Windows, Mac and Linux. You can manually update once installed using
clawdrop upgradePATH Configuration
In order to use clawdrop from any terminal and folder, you can add the clawdrop route to PATH environment. Otherwise, you will need to run clawdrop like:
my/path/clawdrop [command]Windows:
In order to add PATH clawdrop to Windows, you must add the current path of your clawdrop.exe to PATH, you can check where your clawdrop.exe is running the command
clawdrop whereisYou can follow this tutorial to add PATH on Windows.
Linux
In Linux, you should simply move clawdrop to /usr/local/bin, as that directory is PATH default:
tar -xvzf clawdrop-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.tar.gz
sudo mv clawdrop /usr/local/bin/ Mac
Similar to Linux, after you decompress, simply move clawdrop to /usr/local/bin:
sudo mv clawdrop /usr/local/bin/ Checking everything is okay
Once installed, you can run
clawdrop help to view all available commands and check that it works correctly. Note: you can run
clawdrop whereis to print where the executable is on your system. Updates
Clawdrop can be updated manually using two methods:- Simply downloading a new version from the downloads page and ovewriting the old file
- Using
clawdrop upgradeand update directly via command
Authentication
In order to use most of the commands, you will need to grant clawdrop access to your Raccreative Games account. To do this, just runclawdrop auth, this command will open a new url where you will be able to generate a new API Key and grant access. 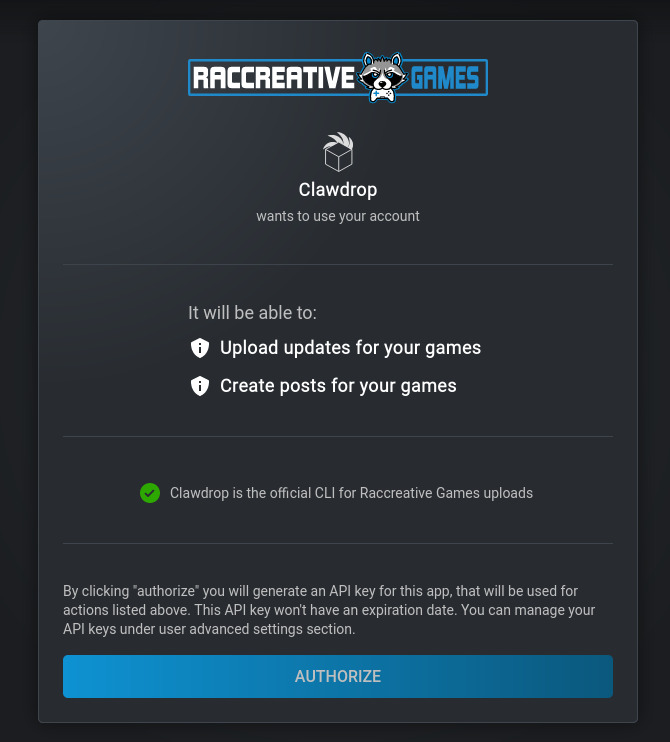
You will be able to manage your API Keys under user advanced settings.
If your Clawdrop CLI is not authorized, it will print an error everytime you try to run a command that needs authorization.
Once this step is done, the API Key will be saved locally until it expires or manually removed using
clawdrop logoutYou can use
--key flag to specify an existing API Key when running the auth command, instead of generating a new one. Setting up a target game
Clawdrop offers the possibility to set an active target game, so every command runs over that game.To set a target game, simply use
clawdrop set [game-id or game-url-slug]If you don't know the id or slug of your game, you can use
clawdrop list to show a list of all the games you are authorized to upload builds, there you will see the ID and more useful data about the game.  You can remove the target game running
You can remove the target game running clawdrop unsetIf you don't want to set a target game, you can simply specify the ID of the game each time you run a command using the
--id flag. Uploading builds
The main command for clawdrop that will be used to upload builds is:clawdrop pushsyntax:
You have multiple ways to use clawdrop push, but there is a shorthand for quick use:
clawdrop push id:os/exe:version- id: The id of the game you want to push. Optional if you have a game already set as active target. (If you don't know the id of your game, you can use
clawdrop listfor a list of your games and info) - os: The operating system of the game you are uploading. Values are "windows", "linux", "mac" or "html"
- exe: The name of the executable file of the game, needed to build the manifest.json. Example "game.exe"
- version: The new version of the build you are uploading, example: 1.2.0. Optional, it will automatically bump configured target game version if exists (you can prevent this using
--no-bumpflag). If no version specified it will be set as 0.0.1.
clawdrop push 42:windows/myGame.exe:1.5.4Beside that, you can omit the shorthand and use common parameters alternative using --id, --os, --version and --exe.
To specify the path of the build you can use
--path, it will use the current folder if no path specified. You can upload freshly new builds to any system if no one exists (example upload first linux version)
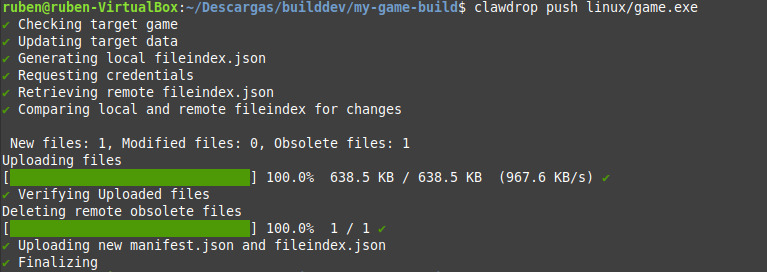 What does it do:
What does it do:Clawdrop will by default upload only chunks of the files that changed or are new, and delete those that are obsolete in new versions. In other words, it will create a differential upload. It uses rac-delta, our own delta patching protocol under the hood to achieve this.
If you simply want to upload everything, you can use
--force flag, this will upload all contents withing the current folder or specified path, except --ignore files that will be explained below. ignoring files:
You can use the
--ignore flag to specify files that won't be uploaded and will be ignored within the whole progress. Example
--ignore '.json' this will ignore all json files that are in the folder. You can also ignore folders the same way using
--ignore 'folder/'Creating game posts
Game post are able to be created using clawdrop. This could be useful if you plan to generate patch notes for your fans o some announcements, and automate them after a build push.The command example is
clawdrop post --id 42 --title 'Patch notes 1.0.3' --body 'body text or ./body.txt' --cover './image.png' --slug 'patch-notes-1-0-3'- id: Id of the game, if you don't know the ID of your game, you can use
clawdrop listto show a list of your authorized games - title: The title of the post
- body: The text of the post, can be specified in plain text or as route for text file
- cover: The cover image of the post (optional), must be a route for image file
- slug: The url slug for the post (optional)
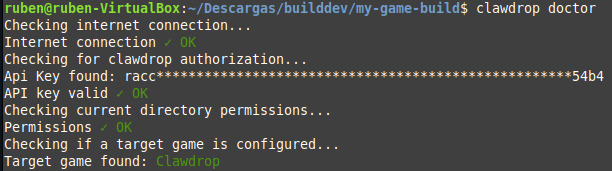
Doctor
Doctor is a small command that will do an environment diagnostic checking:clawdrop doctor- Internet conection is OK
- User is authorized
- Has write permissions
- If there is a target game or not